In all three countries, the project supported implementation of quality improvement (QI) teams, although the approach varied by country. Midline and endline results showed that QI teams involving staff from multiple levels of the supply chain are an effective way to promote data-use, problem solving, communication, and motivation and can significantly improve supply chain practices, resulting in better product management outcomes.
In Malawi, the QI teams intervention is called Enhanced Management (EM) and includes multi-level teams that meet to review data collected by cStock. District product availability teams (DPATs) meet quarterly and include program coordinators, pharmacy staff, and cluster supervisors. Health facility product availability teams (HPATs) meet monthly and include the cluster supervisor, HSA supervisor, and HSAs.
In Rwanda, QI teams meet monthly and participants include: cell coordinators, health center pharmacists, CHW Supervisors, data managers, and district coaches. During meetings, the groups review data collected by cell coordinators during their supervision visits to CHWs and use this data to identify issues and track progress toward objectives set at a previous meeting.
In Ethiopia, many elements of the QI team were incorporated into existing monthly meetings, leading to better use of resupply procedures through problem solving and action planning, although the model was not driven by the use of data, which was not available for that purpose.
Effectively Supporting Resupply Procedures with a QI Approach: Elements and Outcomes
SC4CCM identified the essential elements and intended outcomes of a QI team approach that were common among the teams that the project worked with.
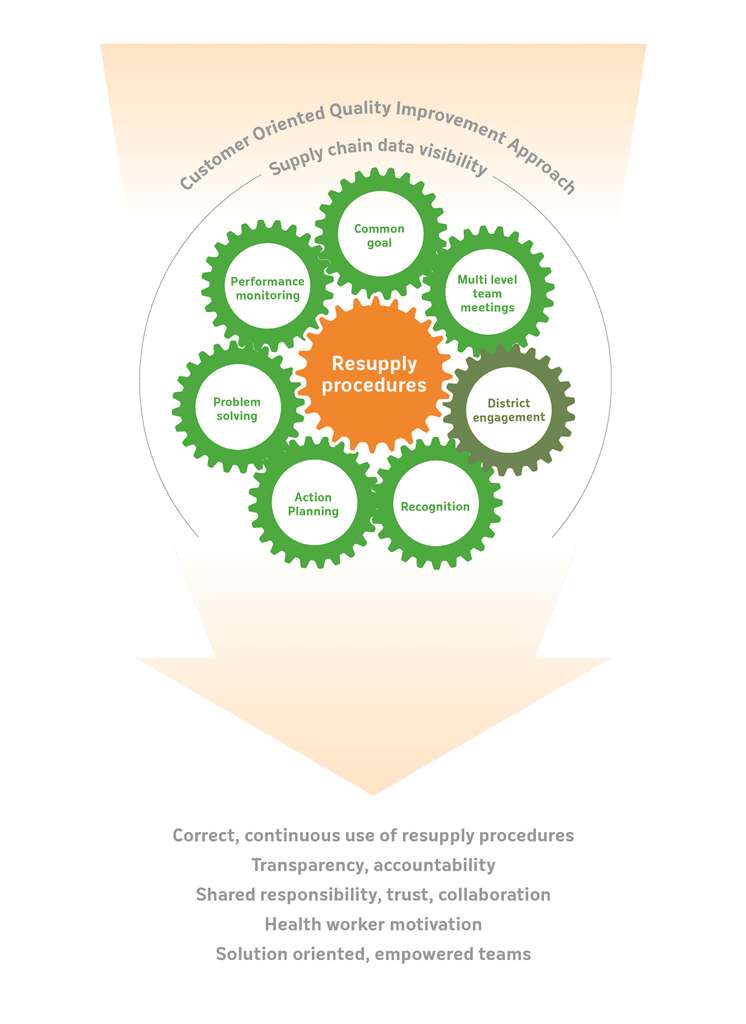
Read more about QI Teams in SC4CCM’s Findings on Strengthening Community-Level Supply Chains Report.

